He focused on studying play and its role in developing children's mental and social abilities, leaving a significant legacy in our understanding of the learning process and child development. His theories are still influencing educational practices worldwide.
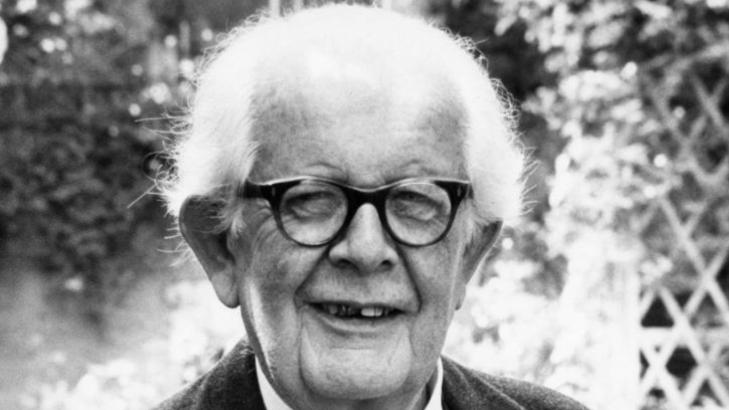
Jean Piaget's Childhood and Upbringing
- He was born on August 9, 1896, in Neuchâtel, Switzerland, and passed away on September 16, 1980, in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Piaget was very close to his paternal grandfather, who was a prominent linguist. His grandfather's intellectual influence was evident in Piaget's early interest in knowledge and language.
- Piaget was greatly influenced by his parents, who were well-educated and interested in science and the arts. They supported their son's academic endeavors and encouraged him to pursue his scientific interests.
- At an early age, Piaget showed a keen interest in natural sciences. At the age of ten, he published his first scientific article about an albino sparrow in a local ornithology magazine.
- He was an outstanding student throughout his childhood. He studied at the University of Neuchâtel's Faculty of Science, where he specialized in biology and psychology.

Jean Piaget Biography
- Piaget is regarded as one of the 20th century's leading figures in developmental and educational psychology. He studied natural sciences and psychology at the University of Neuchâtel and obtained his PhD in psychology from the University of Zurich in 1918.
- He began his academic career as a psychology professor at the University of Zurich and the University of Geneva. Piaget concentrated his research on studying child development and the learning process.
- He presented the Genetic Epistemology theory, which clarifies how children acquire knowledge and thought processes. His theory is based on cognitive constructivism, where Piaget believes that children acquire knowledge on their own through experiences and interactions with their surroundings.
- Piaget's work has significantly impacted education, psychology, and evolutionary biology. Among his important books are Knowledge and Developmental Cognitive, Thinking and Language, and The Theory of Learning and Knowledge Development.
- During his scientific career, he received numerous awards and honors and established research centers such as Geneva's International Centre for Genetic Epistemology. His scientific legacy remains a valuable reference for understanding child development and the educational process, with his ideas still influential today in education and psychology.
Jean Piaget's Career
1. Academic Work Beginning
Piaget started his academic career as a psychology professor at the University of Neuchâtel in 1918, having received his PhD in psychology from the University of Zurich.
2. Research and Teaching at the University of Geneva
Piaget later worked at the University of Geneva, and he is considered one of the most prominent figures in developmental and educational psychology in the 20th century.
3. Piaget Studied Natural Sciences and Psychology at the University of Neuchâtel
He earned his PhD in psychology from the University of Zurich in 1918 and began his academic career as a professor of psychology at the University of Neuchâtel. He also worked at the University of Zurich and the University of Geneva.
4. Piaget's Works Had a Major Influence
Piaget's works have significantly impacted education, psychology, and evolutionary biology. Among his important books are Knowledge and Developmental Cognitive, Thinking and Language, and The Theory of Learning and Knowledge Development.
5. Piaget Received Several Awards and Honors
Piaget received numerous awards and honors and established research centers such as Geneva's International Piaget Centre for Cognitive Studies. His scientific legacy remains a valuable reference in understanding child development and the learning process, and his ideas continue to influence education and psychology today. Additionally, he was a psychology professor and founded the International Laboratory for Psychology and Education.
6. Piaget Published Numerous Books and Research Papers
Piaget published several books and research papers that addressed child development and the learning process, including Knowledge and Developmental Cognitive, Thinking and Language, and The Theory of Learning and Knowledge Development.
7. Piaget's Theories Influenced Education and Psychology
Piaget's theories and research methodology significantly impact psychology and education. His writings are also regarded as a key source when examining child development and the learning process. Piaget is still an influencer in research and educational practices today.
8. Piaget Established Research Centers
Piaget established research centers such as Geneva's International Piaget Centre for Cognitive Studies, which promotes research and education in cognitive development and learning.
Jean Piaget Achievements
1. Genetic Epistemology Theory
One of Piaget's most important contributions was the genetic epistemology theory. This theory holds that children's thinking and knowledge develop in sequential stages. Piaget classified four main developmental stages: the sensorimotor, the preoperational, the concrete operational, and the formal operational stage.
2. Mental Formation and Knowledge Construction
Piaget contributed to our understanding of how children form their minds and construct their knowledge. According to his theory, children acquire knowledge through their personal experiences and interactions with their surrounding environment. This means that children are not merely information recipients, they are also active in constructing their own knowledge.
3. Logical Reasoning and Practical Thinking
Piaget demonstrated the importance of logical reasoning and practical thinking in children's development. He found that children grow their capacity for practical thinking in phases, gradually becoming more structured and abstract in their thought processes.
4. Play and Learning
Piaget emphasized the importance of play in the learning process and child development. He considered play a crucial means of interacting with the environment and experimenting with new ideas and concepts.
5. Play and Learning
Over the decades, Piaget's influence on psychology and education has remained strong. Important research centers, such as Geneva's International Piaget Center for Cognitive Studies, were established to promote research and learning in cognitive development and learning.

Challenges Faced by Jean Piaget
- Piaget's scientific career was not easy. One of the biggest challenges he faced was the resistance and skepticism he ran into when presenting his developmental theory. Some found it difficult to accept the idea that children go through distinct developmental stages in their thinking and knowledge because it went against the conventional theories of the time.
- Many scientists and researchers questioned and criticized Piaget's theory. Some critiques were directed at key concepts in his theory, such as the genetic development stages and the role of play in learning. However, Piaget responded to these criticisms with modifications and developments in his theory.
- There were difficulties in implementing Piaget's theory in educational settings. It was particularly difficult at first to put the theory's concepts into practice in classrooms and create educational programs that addressed children's developmental stages because there wasn't a lot of empirical data.
- Piaget faced procedural and methodological difficulties in conducting his research and experiments. Experiments required a lot of time and effort to conduct, gather, and analyze data. Additionally, some other challenges related to the methodologies used and the difficulty of assessing factors influencing children's development led to criticisms regarding some of his statements and behaviors and accusations of violating safety standards in his studies.
Jean Piaget Impact
- The world has greatly benefited from Jean Piaget's contributions in various domains, which have altered our knowledge of children's cognitive development and learning. One of Piaget's most significant contributions is his genetic development theory, which forms the basis of psychology and education. This theory established strong guidelines for comprehending children's cognitive and developmental growth across a range of age groups.
- His theory has greatly influenced the creation of instructional strategies and curricula. He significantly contributes to the shift in educational approaches from focusing on memorization and rote learning to understanding and active knowledge construction by emphasizing the role of children as builders of their own knowledge and learning through interaction with their environment.
- Piaget's theory and its interactions with other currents in cognitive psychology have expanded the fields of cognitive research and studies. This research has led to further exploration of concepts related to learning, thinking, logical reasoning, and their development over the lifespan.
- Jean Piaget's impact extends beyond psychology and education to various fields. His theories and research have impacted human development, embryology, genetics, neuroscience, and developmental neuroscience.
- Many educational policies and practical applications demonstrate Piaget's influence. His theories and research have helped improve teaching methods and develop curricula, influenced early childhood education, and advanced teacher training programs. His achievements have inspired many young entrepreneurs to pursue their dreams and change the world.
Jean Piaget's Famous Quotes
- “The principle goal of education is to create men who are capable of doing new things, not simply of repeating what other generations have done—men who are creative, inventive, and discoverers. The second goal of education is to form minds which can be critical, can verify, and not accept everything they are offered.”
- “Children have real understanding only of that which they invent themselves, and each time that we try to teach them something too quickly, we keep them from reinventing it themselves.”
Jean Piaget's Awards and Honors
Jean Piaget received numerous awards and recognitions throughout his distinguished career, including:
- Balzan Prize (1979).
- Erasmus Prize (1972).
- Prize from the Catholic University of Leuven (1971).
- Medal of Honor for Culture and Arts (France, 1962).
- Award from the American Psychological Association (1955).
- Honorary Doctorate from Columbia University (1955).
- Honorary Doctorate from Oxford University (1962).
- Honorary Doctorate from Harvard University (1965).
- Additionally, Piaget has been honored by having his name associated with various psychology awards and recognitions, such as the Jean Piaget Award from the International Society for the Study of Behavioral Development (ISSBD), the annual Jean Piaget Lecture from the European Society for Developmental Psychology (ESDP), and the Jean Piaget College at the University of Neuchâtel in Switzerland.





Add comment